
Magnesium (Mg) is considered an essential nutrient that is required for the normal development of a crop. Along with Sulphur (S) and calcium (Ca), it belongs to the secondary macronutrients. As it is a mobile element within the plant, symptoms of its deficiency first occur in older leaves. Cereals (maize), potatoes and legumes are considered crops that are highly susceptible to magnesium deficiency.
1. Basic functions of Magnesium
Magnesium is a crucial nutrient in the following processes:
- Photosynthesis: Magnesium is considered one of the essential building blocks of the chlorophyll molecule.
- ATP formation in chloroplasts.
- Enzyme activation: ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBP) is a key magnesium-controlled enzyme. This enzyme is quite important for the process of photosynthesis.
- Transportation of phosphorus.
- Transportation of carbohydrates: Magnesium has an important role in the transportation of carbohydrates within the plant. A sufficient amount of this element is required in order for carbohydrates to be satisfactorily transported to growth tissues. Therefore, it is logical that in magnesium deficiency, the onset of symptoms of the aerial part must be preceded by the inhibition of the root system growth.
- RNA production – protein synthesis.
2. Availability
Magnesium is ingested by the plant as a divalent Mg2+ ion and transported both through the wood (30 ppm) and the filter (100 ppm).
The forms in which magnesium is found in the soil are the following:
- Mg2+ soil solution – a form that is readily available for plants.
- Bound form in clay minerals – (slowly-available form).
- Bound form in soil organic matter.
- Bound form in primary soil minerals – (non available form).
Soil pH greatly affects the availability of magnesium in the soil. In soils with low pH values, the solubility of magnesium is reduced, making it less available. In addition, Magnesium has a competitive relationship with the cations of Potassium, Calcium, Manganese and Ammonium.
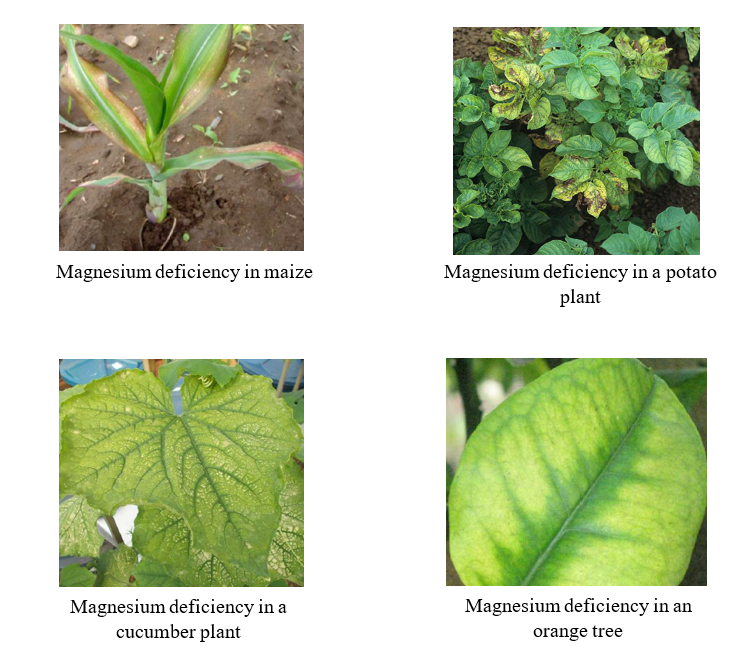
3. Magnesium deficiency
Since magnesium is a mobile element within the plant, symptoms of its deficiency first occur in older leaves. Common symptoms of magnesium deficiency (Mg2+) are:
- Mesoneuric chlorosis of the leaves.
- Drying – wilting.
- Increase in leaf photosensitivity.
- The symptoms increase with the increase of light intensity.
- Increased ratio between aerial part and root system.
- Severe suspension of sugar transportation to nutrient attracting centres.
- Weakening of resistance to abiotic and biotic stress.
Crops vary in sensitivity to low soil magnesium. Cereals (maize), potatoes and legumes are considered crops that are highly susceptible to magnesium deficiency.
4. Tips for preventing magnesium deficiency
Firstly, we suggest that you conduct a soil analysis of your field every two years, so that you have a complete picture of the nutrient levels. Compare your yield goals with the availability of your nutrients and discuss the available options with your agronomist. It is important to apply the right amount of magnesium, at the right rate, always using the right product, as there is a fine line between nutrient deficiency and toxicity.

Viomix Mg is an ideal liquid fertiliser for a wide range of crops that are demanding in magnesium, as it contributes to achieving a balanced nutrition. This product contains 14% magnesium complex, 12% nitrogen and other trace elements. It is applied on the leaves at a dose of 3 L / tn. More information about the product’s user guide can be found in the “Products” tab on our website.

Viomix CaO – MgO is a liquid foliar fertiliser, adapted to all crops that are demanding in magnesium, as it contributes to the achievement of a balanced nutrition. It contains 17% calcium complex, 5% magnesium and 10% L – amino acids. It is applied on the leaves at a dose of 3 L / tn. The pH of the fertiliser is 5.5. More information about the product’s user guide can be found in the “Products“ tab on our website.

Nitromag is a liquid magnesium nitrate fertiliser, that contains 10.5% nitrogen and 13.5% magnesium. It is acidic, with a pH of 3 – 4. It is mainly applied by drip irrigation at a dose of 30 – 50 L / stremma, but also by foliar application at a dose of 3 – 5 L / t. More information about the product’s user guide can be found in the “Products” tab on our website.
Other magnesium nutrition products our company offers are:
Phyto Mag 10.5 – 0 – 0 + 15.5 MgO (Magnesium Nitrate).
Nitromix (Calcium nitrate and magnesium nitrate solution).
Kizerite (Granular fertiliser for basic fertilisation with 25% magnesium).
